
September 6th, 2022 • Payments
Payments in Marketplaces - The 6 Key Considerations for Success! 💳
The expansion of marketplaces has allowed the emergence of integration of payment services.
September 13th, 2022 • Payments

As consumers, perhaps you have noticed that many non-financial companies have launched payment services, specifically debit or credit cards. Major brands from various industries, such as Apple, Uber, and Ikea, have taken the plunge and launched their own card programs for their customers. You may not know it, but by using one of these services, you have probably benefited from the advent of Card-as-a-Service. Of course, the concept of white-label or partnered credit cards is not new. Many department stores have them, and airlines probably provide the best-known use case for these products. However, new non-financial companies are launching creative and innovative payment cards, expanding into untapped market segments, and capturing market share. These brands can now do so thanks to the advent of Card-as-a-Service providers.
Financial services players and brands that recognize the complexity of creating a payment card program are increasingly seeking providers that facilitate issuing and processing cards. Skaleet, provider of a Core Banking Platform for payment and e-money institutions in Europe, shares its feedback on the Card-as-a-Service market.
The concept of “white label” credit cards is based on a partnership between a bank and a company, with traditional banks developing and supervising the cards. But every time an airline wants to issue a new card with a new screening process, limits, or rewards, they have to renegotiate terms with the issuing banks, work out the details, and build everything from scratch. The process usually takes two years. On the other hand, with CaaS players, you can create your own card programs in a matter of weeks, as these providers offer turnkey solutions while automating the entire payment process, from issuing cards to processing payments, not to mention compliance management and risk management. They create physical and virtual cards, take care of “know your customer” obligations and anti-money laundering procedures, and prevent fraud. This allows companies and brands to customize their own card programs while testing new offers and experiences and increasing brand awareness.
The traditional card issuing process is complex and costly, with numerous regulatory compliance requirements. Most of them result from a partnership between a large traditional bank and a company. This is where Card-as-a-Service providers make a big difference. These players offer financial and non-financial companies a modular and turnley card issuing solution with next-generation back-ends. The proceeds from the cards are posted and accessible via a set of available APIs. CaaS providers will work diligently on payment card issues and offer a wide variety of features for card issuing, processing, and management, including underwriting, customer service, bank integration, and associated personalization, tokenization, authentication, and compliance (3DS and PSD2), risk management and KYC, physical/virtual card issuing and distribution, card network membership (Visa or Mastercard), or access to an electronic money license (EMI). These features can be handled by a single financial institution with a banking license and payment processing capabilities or by a fintech company partnering with an issuing processor, payment license provider, and other partners such as cloud providers.
The fintech ecosystem has become a real team sport in recent years. CaaS is an integral part of this movement, as is embedded finance, “collaboration is the new competition.” With the opening up of back-end systems and the development of Open APIs, the cloud, and the growth of the payments industry, many companies from core non-financial industries are increasingly engaging in payments to increase profitability and deliver an increasingly unified customer experience. Banking-as-a-Service, Payment-as-a-Service, and Embedded Finance confirm that the collaborative model is now firmly established in the banking landscape. According to a 2022 study, “74% of consumer payments will be processed by non-traditional financial services institutions by 2030.” As more and more brands and non-financial businesses seek to incorporate payments into their offerings, banks need to seize the technology and processing opportunity to ensure they are not left behind.
Basically, CaaS players are primarily facilitators that enable payment offerings to be incorporated into non-financial experiences. For example, Marqeta, via its API, has enabled Uber to issue its own physical and virtual payment cards with the ability to enable and disable settings. In the same vein, the Finnish fintech company, Enfuce, can produce all sorts of white label cards in 8 weeks: debit cards, prepaid cards, gift cards, and credit cards, all while incorporating management features into the application.
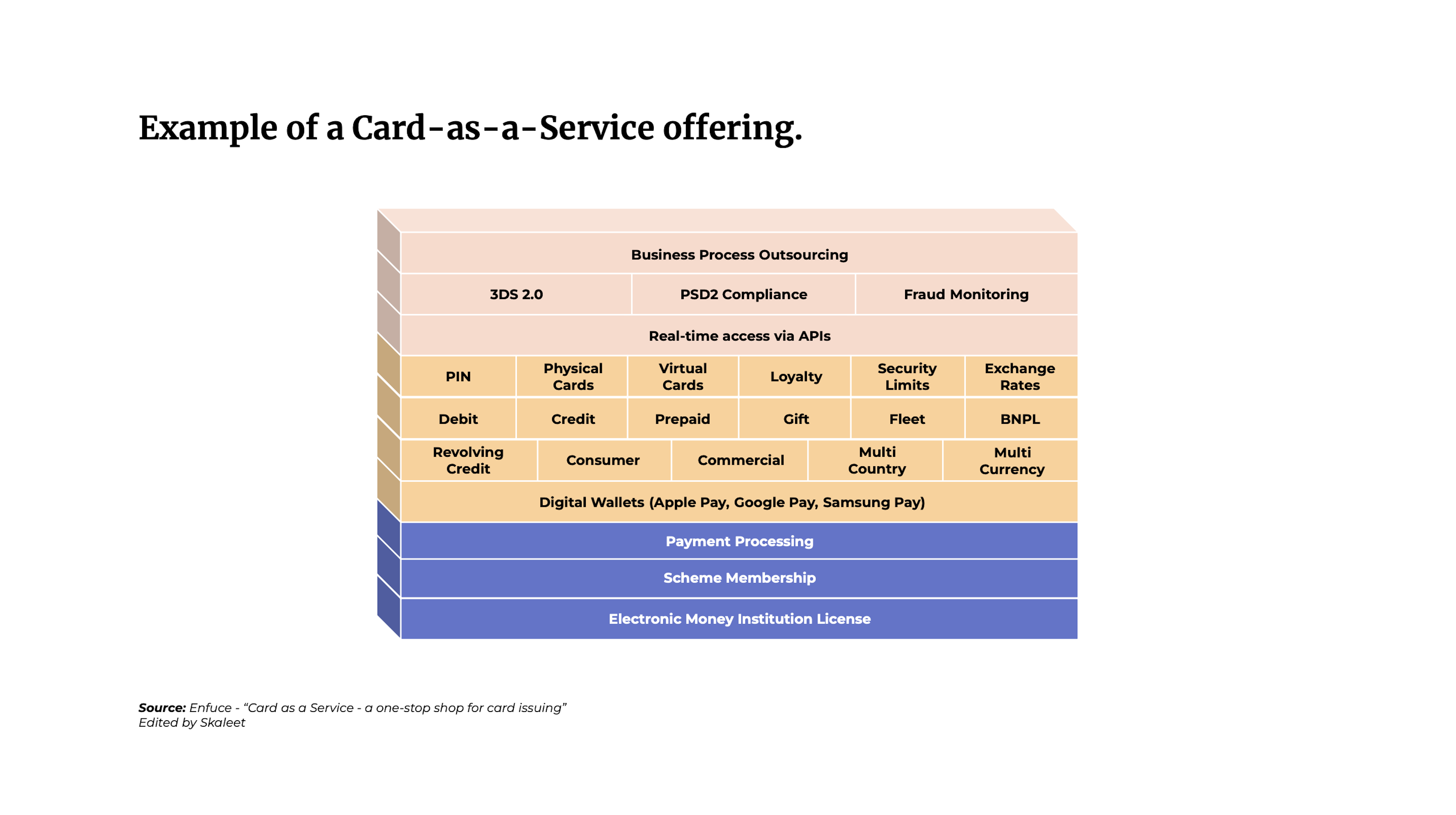
All CaaS customers seek to create, launch and manage a card program without mastering the business knowledge and the intricacies of payment compliance and technology. One of the major attractions of using a CaaS solution is the access to payment data and, more specifically, to cardholder data and established programs. This information is used to create additional promotional or cashback programs to give customers relevant offers directly in the application and linked to a bank account. Over time, companies relying on CaaS solutions are looking to gradually take back some of the processes as they grow. These turnkey solutions allow financial and non-financial players to accelerate time to market and ensure cost efficiency while allowing them to test their new payment card solutions. CaaS providers will be responsible for ensuring regulatory compliance, smooth operations with card networks, BIN provisioning, collections, and settlement on behalf of its customers. This allows brands and companies to gain business knowledge and invest heavily in IT infrastructure that requires substantial automation. Indeed, CaaS providers can reduce their processing costs through economies of scale due to having many customers using their solution. This will also allow them to develop new and more interesting capabilities and features to better diversify their card offerings compared to the competition.
CaaS solutions also allow you to create specific solutions tailored to underserved market segments or those with unique use cases. This divides existing markets into many more markets and provides an opportunity to tap into a new customer niche. For example:
Creating specific solutions for specific markets leads to the possibility of creating new features associated with payment cards, the value proposition a company wants to create, or the lifestyle choices of a customer segment. We find new features such as financial management tools called PFM, real-time notifications when we make payments or when we reach limits, the use of payment data via Open Banking, the tokenization of payment cards to make purchases with applications such as Apple Pay and Google Pay, the integration of loyalty and cashback programs, the use of multi-currencies to pay in different currencies, or make installment or deferred payments (BNPL).
Today, with the market completely open and new players offering credit cards, the options for business models, value propositions, and technology infrastructure to make these next-generation financial services available are vast. Several vendors and a wide range of organizations are available to create a CaaS solution. However, they are all positioned differently with their own business models and products that fit in different places in the banking value chain:
Skaleet supports payment institutions that want to launch new card products and process them as part of their strategy to expand into new market segments to increase revenue streams. With the Core Banking Platform’s flexible configuration, any financial institution can launch various payment card models, including BNPL, corporate cards, and payment wallets. You will be able to create all the cards you want, manage real-time authorizations, process transactions, and manage customer accounts to reduce the technical resources and costs associated with starting this business. Please get in touch with us if your company aspires to become a Card-as-a-Service player.
Innovation. FinTech. Digital Banking. Neobanks. Open Banking. Core Banking. Cloud.

September 6th, 2022 • Payments
The expansion of marketplaces has allowed the emergence of integration of payment services.